Transgender Pride Flag - transgender ftm flag
brainstorming: A group problem-solving method in which each person in a group presents his or her ideas in an open forum, with the purpose to come up with a great number of different ideas.
In the ASN, standards are hierarchically structured: first by source; e.g., by state; within source by type; e.g., science or mathematics; within type by subtype, then by grade, etc.
Illustrated online instructions for making a tetrahedral kite: https://boyslife.org/hobbies-projects/projects/1732/build-it/.

The author acknowledges the support and help from UC Davis RESOURCE advisors Alisa Lee, Travis Smith and Jean VanderGheynst. He also thanks the RESOURCE fellows for their helpful comments during the writing of the activity.
Engineering never has one answer and no perfect design exists. Engineers research all information accessible to them and identify multiple design strategies (in our situation, kites) that may work for their needs. Then engineers select the most promising design to build and test. Testing is a key step to enable engineers to learn vital information about their designs and helps them to identify unforeseen problems and weaknesses. For instance, in this activity, if a kite does not fly, then students examine potential reasons why it failed. Or if a kite breaks mid-flight, then students may seek to find a sturdier design. It is vital for students to understand that new designs do not have to work the first time, and even if they do, there is usually room for improvement.
Indiana state flagfacts
Kites may seem like toys, but they were once an integral part of weather forecasting, communication and war. Over time, kites have been replaced by airplanes, but their use has taught us a great deal about flight.This early tetrahedron kite design by Alexander Graham Bell shows how the shape can be stacked for flight to use a kite as a test instrument.copyrightCopyright © c. 1905 Alexander Graham Bell, The Bell Family via Wikimedia Commons {PD} https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Early_design_of_a_Tetrahedron_kite_cell,_by_Alexander_Graham_Bell.jpg
Indiana statebird
Through the continuing storyline of the Rockets unit, this lesson looks more closely at Spaceman Rohan, Spacewoman Tess, their daughter Maya, and their challenges with getting to space, setting up satellites, and exploring uncharted waters via a canoe. Students are introduced to the ideas of thrust,...
Engineering Design with Application to Unpowered Flight: Students create a constraints checklist, make sketches and explain their design changes on the Engineering Design with Application to Unpowered Flight Worksheet. Look for evidence that students are thinking through their ideas and designs before construction begins. Encourage students to discuss and share test results of their initial kite designs; pay attention for thoughtful comments. The redesign step of the activity provides an opportunity for further assessment on how students evaluate and improve on their initial designs.
More than 100 pages use this file. The following list shows the first 100 pages that use this file only. A full list is available.
You may be familiar with Alexander Graham Bell for his invention of the telephone, but are probably less familiar with his great interest in achieving flight. One of his first "flying machines" was made using a kite-like design. One of the most interesting shapes he used for his kites was a tetrahedron—a solid-triangular pyramid. This tetrahedron shape can be stacked upon itself to create larger tetrahedrons, much like LEGO pieces can be stacked and combined into a bigger whole.In 1909, Alexander Graham Bell designed this early flying machine composed of 3,393 tetrahedron cells.copyrightCopyright © 1909 Unknown photographer, Wikimedia Commons https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:AEA_Cygnet_II.jpg
Indiana stateflower
Post-Quiz: Administer the four-question Design and Fly a Kite Pre/Post-Quiz again. Compare pre/post answers to assess individual student learning about forces acting on kites in flight and the engineering design process.
Use of the TeachEngineering digital library and this website constitutes acceptance of our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
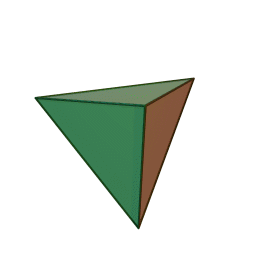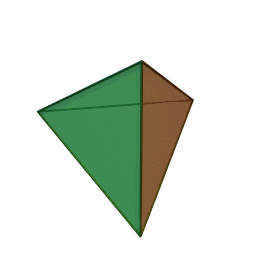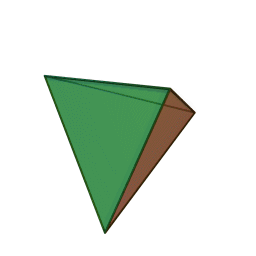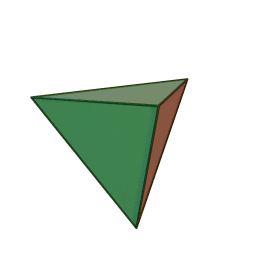
tetrahedron: A three-dimensional shape made of four equilateral triangles. A triangular pyramid. It may also be described has having four triangular faces, six straight edges and four vertex corners.
Building Tetrahedral Kites. (A middle school activity in which student teams construct tetrahedral kites following specific instructions and using specific materials in a limited time period, paying attention to basic manufacturing systems while aiming for team efficiency and product quality. A good source for a basic initial tetrahedral kite design.) TeachEngineering.org.
Class Discussion: At activity (or competition) end, lead a class discussion in which students share their redesign results and gain practice in technical communication. Take note of students' discussion contributions to gauge their engagement and depth of comprehension.
Each TeachEngineering lesson or activity is correlated to one or more K-12 science, technology, engineering or math (STEM) educational standards.
5 facts about theIndiana state flag
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it.
Wind is a force. When it is blowing, you can feel it push you around. If the wind's force can be redirected downwards, you create what is called lift. Lift is a force that causes an object to rise in height, or fly/hover. Lift has a natural "enemy" known as gravity. Gravity is a force that brings things back towards the ground. If not enough lift is created by redirecting the wind and overcoming the force of gravity, an object won't fly. The problem may be rectified by either reducing the mass of the object being lifted (this reduces the force of gravity acting on the object) or increasing the lift to overcome gravity.
The contents of this digital library curriculum were developed by the Renewable Energy Systems Opportunity for Unified Research Collaboration and Education (RESOURCE) project in the College of Engineering under National Science Foundation GK-12 grant no. DGE 0948021. However, these contents do not necessarily represent the policies of the National Science Foundation, and you should not assume endorsement by the federal government.
Consult the Building Tetrahedral Kites activity for details on how to fabricate a basic design for working tetrahedral kites with the potential for further manipulation.
All 100,000+ K-12 STEM standards covered in TeachEngineering are collected, maintained and packaged by the Achievement Standards Network (ASN), a project of D2L (www.achievementstandards.org).
Units serve as guides to a particular content or subject area. Nested under units are lessons (in purple) and hands-on activities (in blue).
What is a tetrahedron shape? (Listen to student ideas.) The tetrahedron is a three-dimensional shape made of four equilateral triangles. It is a triangular pyramid. It has four triangular faces, six straight edges and four vertex corners. (If available, show students a tetrahedral block or an animation of one at https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tetrahedron.gif.)A rotating tetrahedron.copyrightCopyright © 2005 Cyp via Kjell André, Wikimedia Commons https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tetrahedron.gif
Working in teams of four, students build tetrahedral kites following specific instructions and using specific materials. They use the basic processes of manufacturing systems – cutting, shaping, forming, conditioning, assembling, joining, finishing, and quality control – to manufacture complete tetr...
Indiana state flagname
Use of the TeachEngineering digital library and this website constitutes acceptance of our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Since the early days of flight, ideas for flying machines and their wing structures have been extensively tested. The aeronautical engineers of today continue to design new wing structures, now using computers and wind tunnels. To test early wing designs that used the tetrahedron shape, small and inexpensive kites were used. Alexander Graham Bell was one engineer and inventor who designed flying machines and found that generating lift was a problem. To increase lift, which often came at the expense of added weight or lack of structure, he experimented with the tetrahedrons to create structures that were both strong and lightweight. Use of the tetrahedral shape resulted in large kite structures of minimal weight with enough lift to achieve flight, even with passengers and eventually powered flying machines. Kites proved to be a great testing ground for the design and construction of Bell's tetrahedron-based flying machines. The tetrahedron also had the advantage of being a modular design; the tetrahedral "cell" shapes could be stacked and manipulated for more lift and repurposed into many different designs for flight. In this activity, students work as if they are aeronautical engineers, designing, and redesigning wing prototypes.
Indiana state flagcolors
In the activity, students start with a basic tetrahedral shape. Tetrahedrons are both strong and lightweight, which is key for achieving flight. Covering two sides of the tetrahedron shape can help create lift. Lift is the upward force on the tetrahedron created when wind hits the tetrahedron cell and is redirected downward. Multiple sets of smaller tetrahedrons can be connected into one larger tetrahedral kite, and the combined lift acting on each of the smaller tetrahedrons can overcome the weight of the entire kite. This usually enables the kite to take flight.
constraint: A limitation or restriction. For engineers, constraints are the requirements and limitations that the final design solutions must meet.
3-5-ETS1-2. Generate and compare multiple possible solutions to a problem based on how well each is likely to meet the criteria and constraints of the problem. (Grades 3 - 5)
Students get a running start to launch their tetrahedron kite.copyrightCopyright © 2015 Denise Jabusch, University of California Davis
Pre-Quiz: Administer the four-question Design and Fly a Kite Pre/Post-Quiz to assess students' prior knowledge of forces acting on kites in flight and the engineering design process.
Time Required: 4 hours Takes ~ four hours plus drying time; best to run in multiple sessions to permit glue drying between sessions.
Who made theIndiana state flag
Indiana state flagmeaning
3-5-ETS1-1. Define a simple design problem reflecting a need or a want that includes specified criteria for success and constraints on materials, time, or cost. (Grades 3 - 5)
Students learn about kites and gliders and how these models can help in understanding the concept of flight. Then students move on to conduct the associated activity, during which teams design and build their own balsa wood glider models and experiment with different control surfaces, competing for ...
3-5-ETS1-3. Plan and carry out fair tests in which variables are controlled and failure points are considered to identify aspects of a model or prototype that can be improved. (Grades 3 - 5)
The tetrahedron shape is popular for its advantageous strength-to-weight ratio, which means that for a given weight of a structure, in this case tetrahedrons, a large amount of force can be supported, which we call strength. This characteristic is derived from the geometry of the tetrahedron itself.
It helps with construction if students create a template shape for covering the tetrahedrons, such as the covered planes illustrated in the orange color in Figure 2.

